People Suffering from Gout Pain Know Just How Bad It Can Get
Affecting over 3 million Americans each year, gout is a very common illness. Considered a form of arthritis, gout is a complex condition that tends to come and go in patients. Most people who suffer from gout have symptoms come on suddenly and almost always occur at night time. When a patient has high levels of uric acid in their bloodstream, the uric acid runs the risk of turning into urate. Urate can crystallize and move down the bloodstream, typically to the toe region and cause intense pain. Thankfully, a lot is known about gout due to how common it is and it is a treatable condition. Certain people have risk factors that make them more prone to developing gout and many of those risks are preventable.
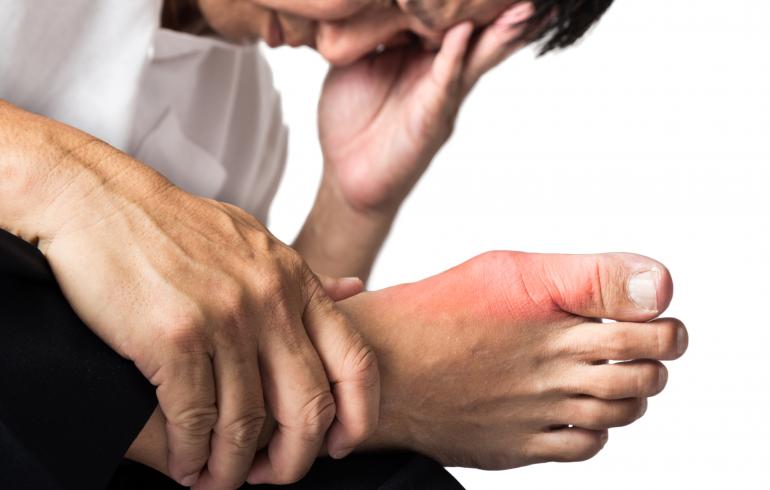
Symptoms and Gout Pain
As previously mentioned, gout pain almost always strikes suddenly, leaving the patient very little warning. Gout pain can occur in any joint, but typically affects the big toe the most. Some other symptoms of gout include:
- Lack of range of motion in joints
- Stiffness or discomfort in joints, sometimes including lumps
- Redness in affected area
- Sudden, intense pain in joints
- Heat in the joints
- Joint swelling
Since gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis, these symptoms are all a result of your body reacting to the white blood cells releasing chemicals in the joint area, which is what is causing the pain. Like many other conditions, symptoms will continue to progress past the initial flare if nothing is done to combat gout relatively quickly.
Causes of Gout
Like it was stated in the introduction, gout is a form of arthritis caused by the body's reaction to urate crystals forming in the joints due to urate in the bloodstream. While this is not completely preventable for all gout sufferers, there are certain risks factors that make someone more prone to developing gout. Some of these risk factors include:
- Being male or a postmenopausal woman - Being a man or going through menopause raises the levels of uric acid in your bloodstream. These are two risk factors that cannot be controlled.
- Family history of gout - Like most conditions, being genetically prone to a disease makes you much more likely to develop the condition.
- Chronic lead exposure
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Having high body fat content or being overweight
- Trauma or surgery to the joint
- Kidney problems
- Diabetes, especially uncontrolled diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High purine diet - Certain foods can raise the levels of uric acid in your blood
Treating Gout
Since gout is one of the most common and frequently mentioned medical conditions, a lot is known about how to treat it. For treating both flares and preventing future attacks, many people take over the counter painkillers to control symptoms. Stronger painkillers may also be prescribed for more serious cases.
If you have frequent gout flares or extremely painful ones, your doctor may prescribe you a drug that allows your kidneys to remove uric acid from your blood more successfully. Drugs also exist that help to hamper the production of uric acid in your body. Regularly drinking water and avoiding certain foods also helps people control symptoms of gout.



